Food systems account for one-third of GHG emissions, a critical issue at the COP28, and triggered FAO's Global Roadmap for Sustainable Food Systems. More than 159 world leaders endorsed the Declaration on Sustainable Agriculture, Resilient Food Systems and Climate Action, and food giants committed to advancing regenerative agri-food projects. In navigating these challenges, the food and beverages industry also leverages sustainable practices for operational efficiencies, cost savings, and new market opportunities, blending environmental responsibility with commercial viability, according to Aptean’s 2024 Food and Beverage Trends Report.

How industry giants are reshaping supply chain ethics
Sustainable sourcing from farm to factory in the food & beverages manufacturing industry
Value chain: upstream
Food & beverage manufacturing
AT A GLANCE
Major food & beverage companies are committing to responsibly sourcing 100% of their key ingredients.
The industry focuses on developing ethical sources, such as alternative proteins and sustainable packaging
Incentives may be strategically tapped to encourage suppliers and farmers to produce sustainably.

Solid verification mechanisms
F&B manufacturers like Coca-Cola, Pepsi and Unilever have committed to sustainably sourcing 100% of their key ingredients. As follow-through, Mondelez and Kraft Heinz implement rigorous third-party supplier qualification processes to ensure compliance with the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) principles. Kraft Heinz partners with external organisations, Sedex (for direct suppliers) and Ecovadis (for indirect suppliers), to monitor potential human rights risks and non-compliances in the supply chain.
Biotech & agriculture
Biotechnological innovations help expand the pool of ethical product sources. Anheuser Busch has been developing alternative protein sources made from saved grains and beer waste. Similarly, Nestle, through its Institute of Agricultural Sciences and partnerships with start-ups, has been focusing on research in plant science and dairy livestock to source more sustainable key ingredients and guide its network in adopting sustainable farming techniques.
Incentivising smart tech
With a USD 42 million investment, Tyson Foods, along with USDA and other partners implements a climate-smart project that focuses on training, incentives and verifications to help farmer and rancher livelihoods through adopting climate-smart practices. As part of this, Tyson Foods’ Climate-Smart Beef Program incentivises producer adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices, while investing in research on how to reduce methane emissions in the beef value chain.
Long-term outlook
As scrutiny over food systems’ environmental impact intensifies, the F&B industry must anticipate and adapt to regulatory and market expectations. Leaders are prioritising operational resilience and adopting regenerative agricultural practices to secure sustainable supply chains. Reporting of compliance with standards, such as the RSPO, GRI and SASB, will also be critical in strengthening consumer trust and navigating evolving regulatory landscapes (like the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (effective in 2024).
FURTHER READING
- Q&A on ESRS (European Commission)
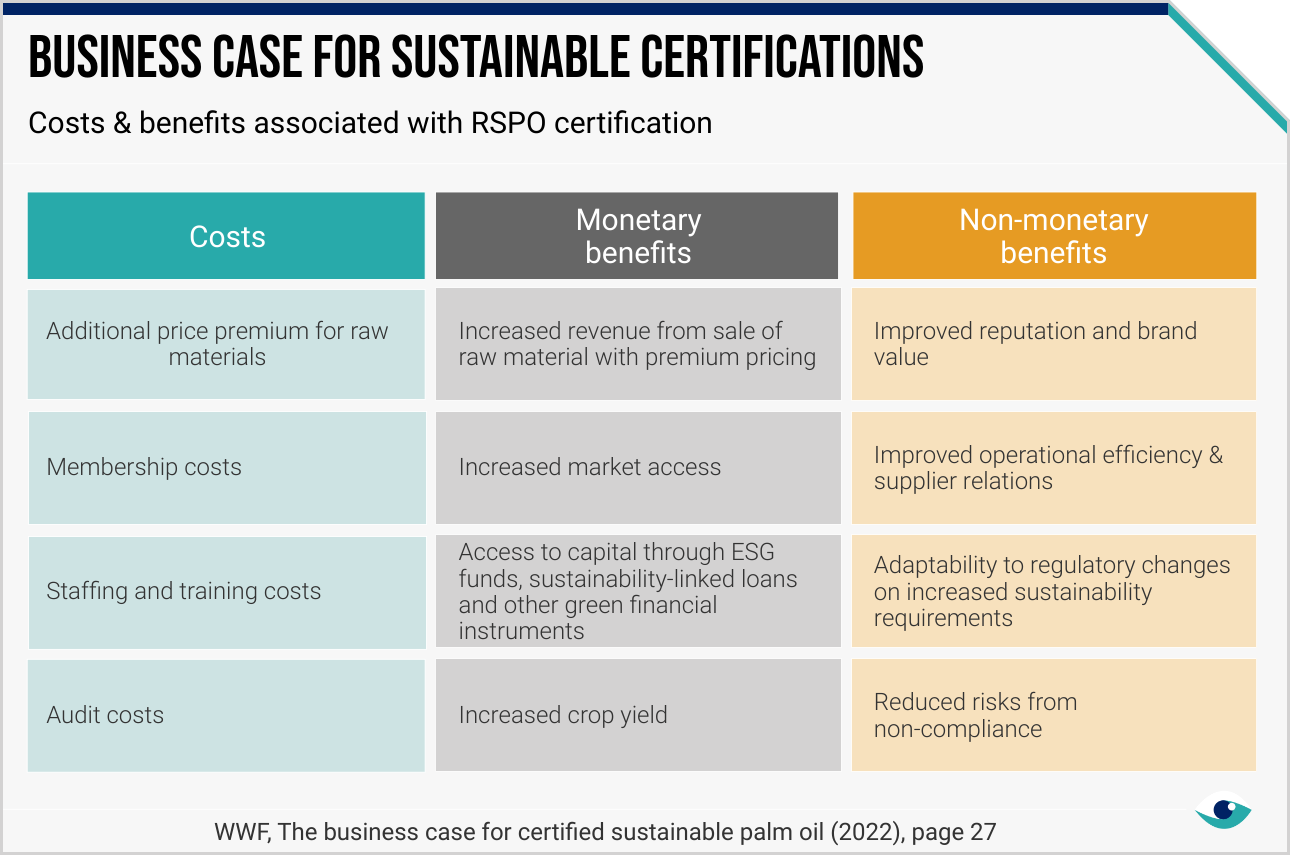
- Certified sustainable palm oil (WWF)
- COP28 food breakthroughs (WRI)
