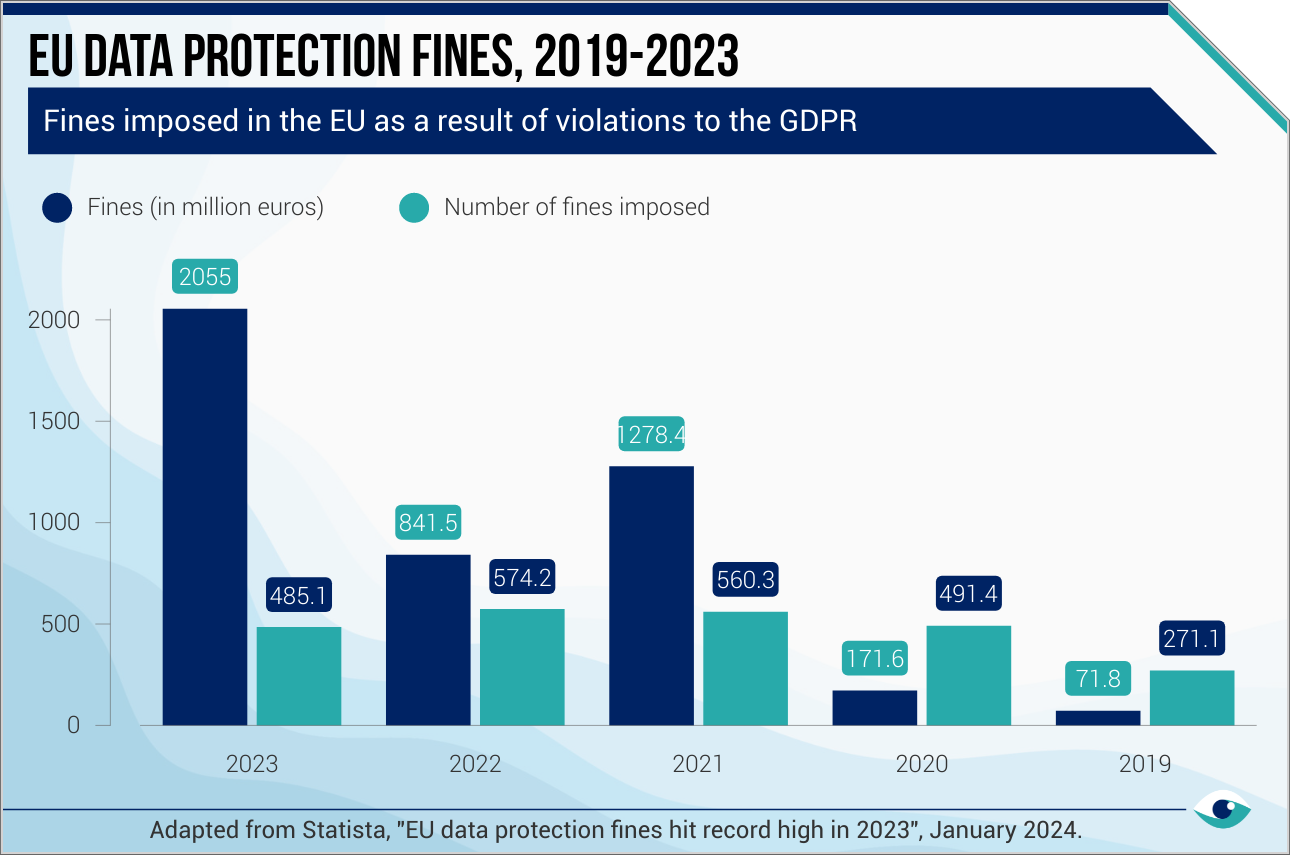
In 2023, the EU levied a record EUR 2.1 billion in fines for violations of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This surge indicates that firms are struggling to protect personal data adequately. The potential penalties for non-compliance can reach up to EUR 20 million or 4% of a company's global revenue, whichever is higher. Consequently, e-commerce firms need to strengthen their data-governance frameworks, which should include implementing clear privacy policies, obtaining explicit consumer consent, enhancing data-protection measures and conducting regular audits.

BACK

Mismanagement of downstream customer data risks hefty fines
E-commerce firms face heightened vulnerability to data-protection fines amid tightening and diverse regulations globally
Value chain: downstream
Consumer durables retail
Publication date: 16 Dec 2024
By Melanie Kramer
AT A GLANCE
Global variation in data protection laws adds compliance challenges for e-commerce firms within consumer durables retail.
With vast access to downstream consumer data, firms lacking strong governance frameworks face significant risks.
Industry best practices include maintaining transparency, securing explicit user consent and implementing stringent data security measures.
Data risks in ecommerce
In 2021, Meta faced a record EUR 1.2 billion fine for unlawful data transfers to the US. This case highlights vulnerabilities within the data-handling practices applicable for e-commerce entities. Amazon is currently contesting a record EUR 746 million fine by Luxembourg's data protection authority. E-commerce firms are particularly susceptible to GDPR violations due to their extensive data collection. As global jurisdictions adopt stringent regulations similar to the EU GDPR, firms must continually adapt their compliance strategies across regions.
Financial risks
E-commerce firms, which handle vast quantities of user data, face significant risks if they fail to comply with data-protection laws. Mismanagement of this data can lead to substantial fines that must be recognised as “expected penalties” under IAS 37, potentially eroding shareholder value. These financial repercussions emphasise the need for e-commerce platforms to maintain rigorous data-protection measures to avoid legal liabilities and uphold their reputation.
Balancing data and privacy
E-commerce firms face the complex task of balancing two often conflicting priorities: leveraging vast amounts of downstream consumer data to enhance user experience through personalised marketing and respecting consumer privacy. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standard for e-commerce emphasises this dilemma, requiring disclosures on how user data is used for secondary purposes and the policies related to behavioural advertising and user privacy. As companies process extensive personal, demographic and behavioural data, the risk of privacy violations increases.

Data and privacy laws
As global data-privacy regulations are anticipated to tighten further, e-commerce firms must maintain vigilance and adapt their data-handling practices accordingly. It is key for firms to establish robust data-governance frameworks and implement proactive strategies, including data minimisation, securing explicit user consent and enhancing transparency in how data is used.
FURTHER READING
- Complete guide to GDPR (European Union)
- GDPR enforcement tracker (CMS)
- Global data protection regulations (PWC)

BACK
